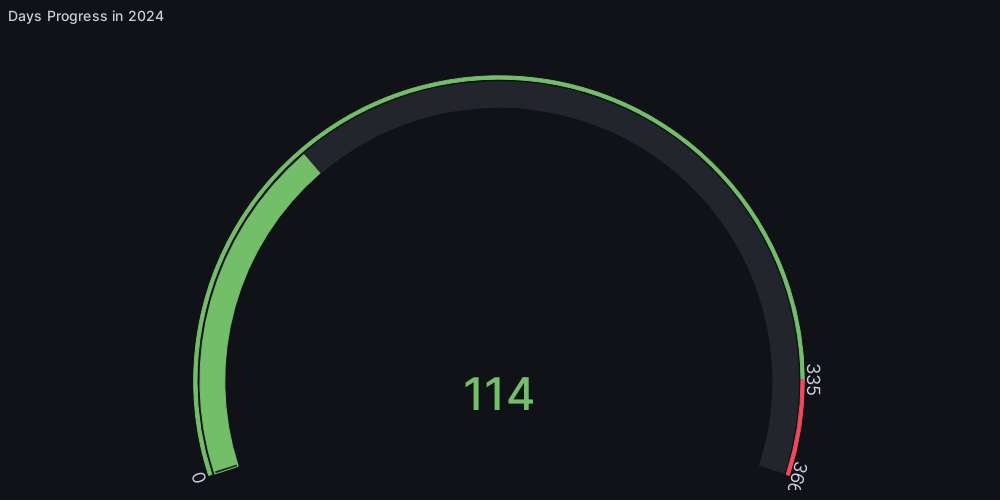
Day of the Year
The number of days left in the year 2023 is calculated by subtracting the current date from the last day of the year, which is December 31st. For example, on January 1st, 2023, there are 364 days left in the year. On February 28th, 2023, there are 334 days left in the year. And so on.
| Month | Days left in year |
|---|---|
| January 1st | 364 |
| February 1st | 334 |
| March 1st | 306 |
| April 1st | 275 |
| May 1st | 245 |
| June 1st | 214 |
| July 1st | 184 |
| August 1st | 153 |
| September 1st | 122 |
| October 1st | 92 |
| November 1st | 61 |
| December 1st | 31 |
You can use this table to plan events, set goals, and track your progress towards your goals. For example, if you have a goal to write a book in one year, you can use this table to track your progress and make sure that you are on track to meet your goal.
This information can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Planning events
- Setting goals
- Tracking progress towards goals
- Understanding how much time is left in the year
- Making the most of each day
For example, if you are planning a vacation, you can use our website to see how many days are left in the year and choose a date that is convenient for you and your travel companions.
If you are setting goals, you can use our website to track your progress and make sure that you are on track to achieve your goals by the end of the year.
If you are simply trying to make the most of each day, you can use our website to see how much time is left in the year and make sure that you are spending your time wisely on the things that are important to you.
Our website is a valuable resource for anyone who wants to make the most of their time in 2023.
Quiz
-
How many days are left in the year on February 28th?
-
How many days are left in the year on April 30th?
-
How many days are left in the year on June 30th?
-
How many days are left in the year on August 31st?
-
How many days are left in the year on October 31st?
Scroll to the bottom of the page for the answers
What does Day of the Year mean?
The day of the year is the sequential number of a day within a calendar year. It is also known as the ordinal date of a day. The first day of the year is day 1, and the last day of the year is day 365 in a non-leap year, and day 366 in a leap year. The day of the year is a useful way to track the passage of time throughout the year. It can be used to calculate the number of days left in the year, to plan events, and to track progress towards goals. For example, if you have a goal to read 52 books in one year, you can use the day of the year to track your progress and make sure that you are on track to achieve your goal by the end of the year.
The day of the year is also used in a variety of other contexts, such as:
-
Science
In science, engineering, and business. In science, the day of the year is used to track the seasonal changes in the Earth’s climate and environment.
-
Engineering
In engineering, the day of the year is used to design and schedule projects. And in business, the day of the year is used to track sales and other financial data.
How many days are there in a year?
There are 365 days in a common/non-leap year.
Common Year
| Month | Days Left in Month |
|---|---|
| January | 31 |
| February | 28 |
| March | 31 |
| April | 30 |
| May | 31 |
| June | 30 |
| July | 31 |
| August | 31 |
| September | 30 |
| October | 31 |
| November | 30 |
| December | 31 |
How many days are there in a leap year?
There are 366 days in a leap year.
Leap Year
| Month | Days Left in Month |
|---|---|
| January | 31 |
| February | 29 |
| March | 31 |
| April | 30 |
| May | 31 |
| June | 30 |
| July | 31 |
| August | 31 |
| September | 30 |
| October | 31 |
| November | 30 |
| December | 31 |
What is the difference between leap years and non-leap years?
There is one key difference between leap years and non-leap years: the number of days in the year. A leap year has 366 days, while a non-leap year has 365 days.
This difference is due to the fact that the Earth’s orbit around the Sun does not take exactly 365 days. It actually takes 365.2422 days. To account for this fractional difference, we add an extra day to the calendar every four years, except for years that are divisible by 100 but not by 400. This is why the year 2000 was a leap year, but the year 1900 was not.
The extra day in a leap year is added to the end of February, which is why February has 29 days in a leap year.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between leap years and non-leap years:
| Characteristic | Leap year | Non-leap year |
|---|---|---|
| Number of days | 366 | 365 |
| Frequency | Every four years, except for years divisible by 100 but not by 400 | Every year that is not a leap year |
| Example | 2000, 2024, 2028 | 2023, 2025, 2027 |
Leap years are important because they help to keep our calendars aligned with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Without leap years, our calendars would gradually drift out of sync with the seasons.
Why do we have 12 months instead of just 10?
The Roman calendar had its origins in the early 8th century BC. It was based on the lunar cycle, and it had 10 months, with a total of 304 days. This calendar was not very accurate, and it gradually drifted out of sync with the seasons.
The months in the Roman calendar were:
| Month | Number of days | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Martius (March) | 31 | Month of Mars |
| Aprilis (April) | 30 | Month of Apru (Aphrodite) |
| Maius (May) | 31 | Month of Maia |
| Iunius (June) | 30 | Month of Juno |
| Quintilis (July) | 31 | Fifth Month |
| Sextilis (August) | 31 | Sixth Month |
| September | 30 | Seventh Month |
| October | 31 | Eighth Month |
| November | 30 | Ninth Month |
| December | 31 | Tenth Month |
The use of a 12-month calendar is rooted in a few key factors:
Lunar Cycle: Early calendars were often based on the 29.5-day lunar cycle, resulting in 12 or 13 months.
Seasons: The Earth’s orbit takes about 365.25 days, leading to a 12-month calendar that aligns with the four seasons.
Cultural Traditions: Many religions and cultures have traditions tied to the 12-month calendar. A 10-month calendar wouldn’t be as accurate or aligned with these factors. While there are other calendars in use, the 12-month Gregorian calendar strikes a balance between lunar and solar cycles, making it widely practical.
What is the history behind our current calendar and how did it evolve?
The current calendar that we use, the Gregorian calendar, has evolved over thousands of years. It is a composite of many different calendars that have been used by different cultures throughout history.
Some of the earliest calendars were based on the lunar cycle, which is the time it takes for the moon to orbit the Earth. These calendars had 12 or 13 months, depending on how they were calculated.
Other calendars were based on the solar year, which is the time it takes for the Earth to orbit the Sun. These calendars had 12 months, with each month corresponding to a different season.
The first known solar calendar was the Egyptian calendar, which was developed around 3000 BC. The Egyptian calendar had 365 days, and it added an extra day every four years to keep the calendar aligned with the seasons.
The Roman calendar was another early solar calendar. The Roman calendar was developed around 753 BC, and it had 304 days. The Roman calendar was not as accurate as the Egyptian calendar, and it gradually drifted out of sync with the seasons.
In 45 BC, Julius Caesar reformed the Roman calendar and created the Julian calendar. The Julian calendar was based on the Egyptian calendar, and it had 365 days. It also added a leap year every four years to keep the calendar aligned with the seasons.
The Julian calendar was used for over 1,500 years. However, it was not perfectly accurate, and the seasons gradually drifted out of sync with the calendar again.
In 1582, Pope Gregory XIII reformed the Julian calendar and created the Gregorian calendar. The Gregorian calendar is the calendar that we use today. It is more accurate than the Julian calendar, and it keeps the seasons aligned with the calendar better.
The Gregorian calendar is the most widely used calendar in the world today. It is used by over 2 billion people, and it is the official calendar of the United Nations and most international organizations.
Here is a summary of the evolution of the current calendar:
- 3000 BC: The Egyptians develop the first known solar calendar.
- 753 BC: The Romans develop their own solar calendar.
- 45 BC: Julius Caesar reforms the Roman calendar and creates the Julian calendar.
- 1582: Pope Gregory XIII reforms the Julian calendar and creates the Gregorian calendar.
The Gregorian calendar is a product of many different cultures and civilizations. It is a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of humanity that we have been able to create such an accurate and reliable calendar system.
How did Julius and Augustus Caesar change our calendar?
Julius Caesar added July to the Roman calendar in 44 BC, and Augustus Caesar added August in 8 BC. Before that, the Roman calendar had only 10 months. Julius Caesar was born in the month of Quintilis, so he renamed it July in his own honor. Augustus Caesar was born in the month of Sextilis, so he renamed it August in his own honor.
The other 10 months of the Roman calendar were:
- Martius (March)
- Aprilis (April)
- Maius (May)
- Iunius (June)
- September (September)
- October (October)
- November (November)
- December (December)
When Julius Caesar added July to the calendar, he also added an extra day to February to make up for the fact that the calendar was still not perfectly aligned with the solar year. He also moved the beginning of the year from March to January.
Augustus Caesar also made some changes to the Roman calendar. He added an extra day to August to make it the same length as July, and he also renamed the months of September, October, November, and December to reflect their new positions in the calendar.
The Julian calendar was used for over 1,500 years, and it is the basis of the calendar that we use today, the Gregorian calendar is a composite of many different calendars that have been used by different cultures throughout history. It is a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of humanity that we have been able to create such an accurate and reliable calendar system.
How many seasons are there in a year?
There are four seasons in a year: spring, summer, fall, and winter. The seasons are caused by the Earth’s tilted axis and its orbit around the Sun.
- Spring: Spring is the season of new beginnings. The days get longer and warmer, and the plants start to grow again.
- Summer: Summer is the hottest season of the year. The days are long and sunny, and many people enjoy spending time outdoors.
- Fall: Fall is the season of change. The leaves change color and fall from the trees, and the weather starts to cool down.
- Winter: Winter is the coldest season of the year. The days are short and the nights are long. In some parts of the world, it snows in the winter.
The start and end dates of the seasons vary depending on where you live. In the Northern Hemisphere, spring begins on March 20 or 21, summer begins on June 20 or 21, fall begins on September 22 or 23, and winter begins on December 21 or 22. In the Southern Hemisphere, the seasons are reversed.
The seasons are an important part of our lives. They affect the way we live, work, and play. The seasons also affect the plants and animals around us.
How many days are there in each season?
Northern Hemisphere
- Spring: 90 days
- Summer: 92 days
- Fall: 90 days
- Winter: 92 days
Southern Hemisphere
- Spring: 92 days
- Summer: 90 days
- Fall: 92 days
- Winter: 90 days
These estimates are based on the astronomical definition of the seasons, which is based on the Earth’s position in its orbit around the Sun. The astronomical seasons begin and end on the equinoxes and solstices, which are the days when the Earth’s axis is tilted most directly towards or away from the Sun.
However, some people define the seasons based on meteorological factors such as temperature and precipitation. Meteorological seasons typically start and end on the first days of the months of March, June, September, and December. Using this definition, the number of days in each season would vary slightly from the astronomical definition.
Additionally, the number of days in each season can also vary depending on the specific location on Earth. For example, in some parts of the world, spring and fall may be shorter than summer and winter.
Overall, the number of days in each season is a complex topic with no single answer. However, the estimates provided above are a good starting point.
| Season | Number of days | Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 90 days | March, April, May | September, October, November |
| Summer | 92 days | June, July, August | December, January, February |
| Fall | 90 days | September, October, November | March, April, May |
| Winter | 92 days | December, January, February | June, July, August |
What is the meaning of solstice?
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countries, the seasons of the year are determined by the solstices and the equinoxes.
The word solstice comes from the Latin words “sol” (sun) and “sistere” (to stand still). This is because the Sun appears to stand still in the sky on the day of the solstice.
The solstices are caused by the Earth’s tilted axis and its orbit around the Sun. On the day of the summer solstice, the Earth’s axis is tilted most directly towards the Sun. This means that the Northern Hemisphere is receiving more sunlight than the Southern Hemisphere. On the day of the winter solstice, the Earth’s axis is tilted most directly away from the Sun. This means that the Northern Hemisphere is receiving less sunlight than the Southern Hemisphere.
The solstices are important events in many cultures around the world. In some cultures, the solstices are celebrated with religious festivals and holidays. In other cultures, the solstices are a time to mark the beginning of a new season.
Here are some interesting facts about the solstices:
- The summer solstice is the longest day of the year and the shortest night.
- The winter solstice is the shortest day of the year and the longest night.
- The solstices are the only days of the year when the Sun is directly overhead at a specific latitude.
- The solstices are the only days of the year when the Sun rises and sets at the same time at the poles.
- The solstices have been celebrated by cultures around the world for centuries.
What are equinoxes?
An equinox is an event that occurs when the Sun crosses the celestial equator, which is an imaginary line that divides the celestial sphere into two equal halves. The equinoxes occur twice a year, around March 20 and September 23. On the day of an equinox, the Sun appears directly overhead at the equator.
The word equinox comes from the Latin words “aequus” (equal) and “nox” (night). This is because the day and night are of approximately equal length on an equinox.
The equinoxes are caused by the Earth’s tilted axis and its orbit around the Sun. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its axis remains tilted at an angle of about 23.5 degrees. This means that one hemisphere of the Earth is always tilted towards the Sun, while the other hemisphere is tilted away. On the day of an equinox, the Earth’s axis is tilted so that neither hemisphere is tilted towards or away from the Sun.
The equinoxes are important events in many cultures around the world. They are often celebrated with festivals and rituals that mark the beginning of a new season. Here are some interesting facts about the equinoxes:
- The equinoxes are the only two days of the year when the day and night are of approximately equal length.
- The equinoxes are the only two days of the year when the Sun appears directly overhead at the equator.
- The equinoxes mark the beginning of spring and autumn in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The equinoxes mark the beginning of autumn and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
- The equinoxes have been celebrated by cultures around the world for centuries.
Answers for the Quiz
- There are 306 days left in the year on February 28th.
- There are 245 days left in the year on April 30th.
- There are 184 days left in the year on June 30th.
- There are 122 days left in the year on August 31st.
- There are 61 days left in the year on October 31st.
}